State-by-State CDL Training Requirements
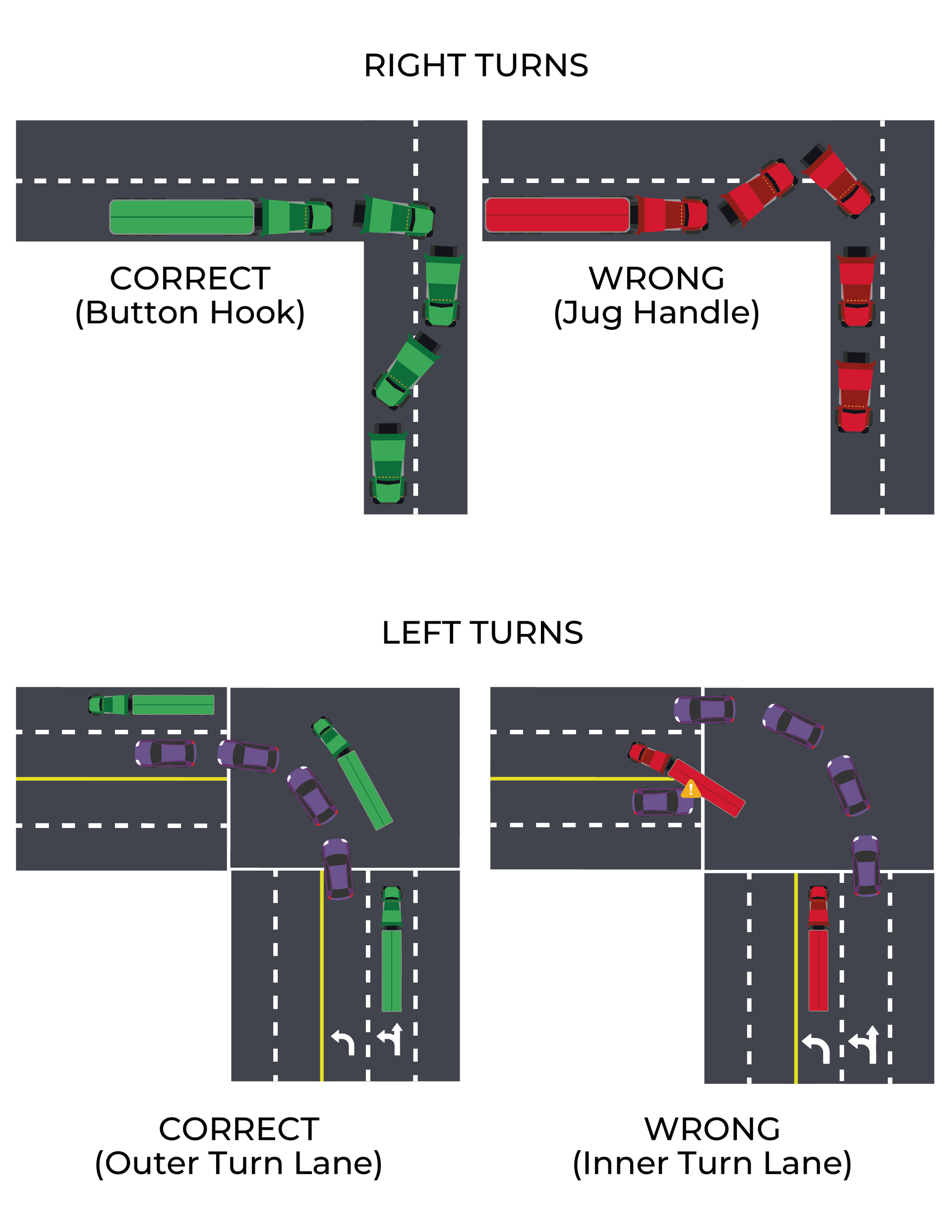












This article provides CDL instructors with a comprehensive guide to teaching space management, a critical safety skill outlined in ELDT Unit 1.2.5. It covers key concepts such as maintaining space ahead, behind, and around the vehicle, with practical tips for turns, crossing traffic, and handling tailgaters.

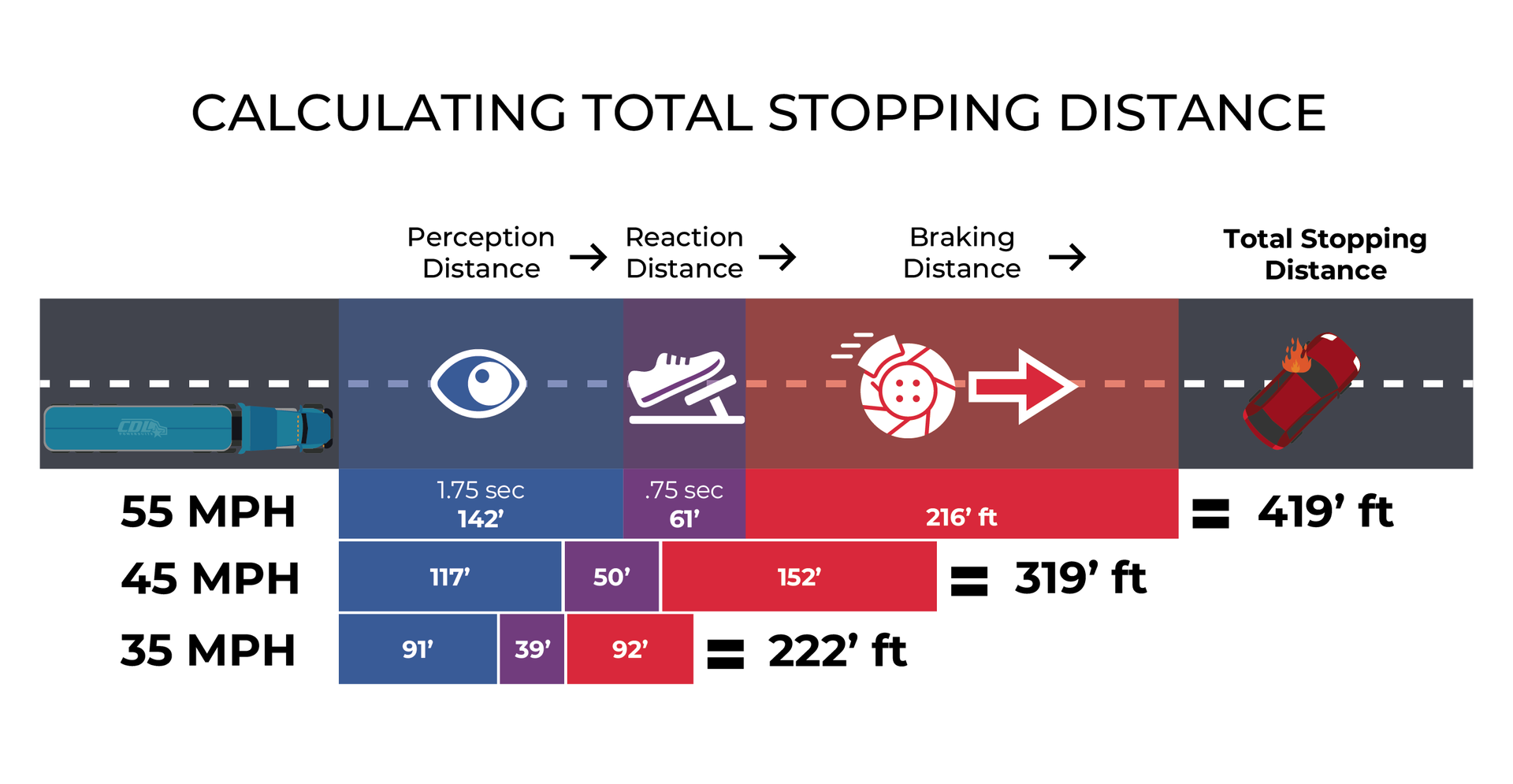
This article equips CDL instructors with practical guidance for teaching speed control and management, a critical component of the ELDT Basic Operating Procedures curriculum. It covers key concepts like stopping distance, the effects of speed and road conditions, and proper downhill braking techniques, including snub braking. Instructors will gain insights and tips for delivering impactful, safety-focused lessons that prepare future drivers for real-world conditions.

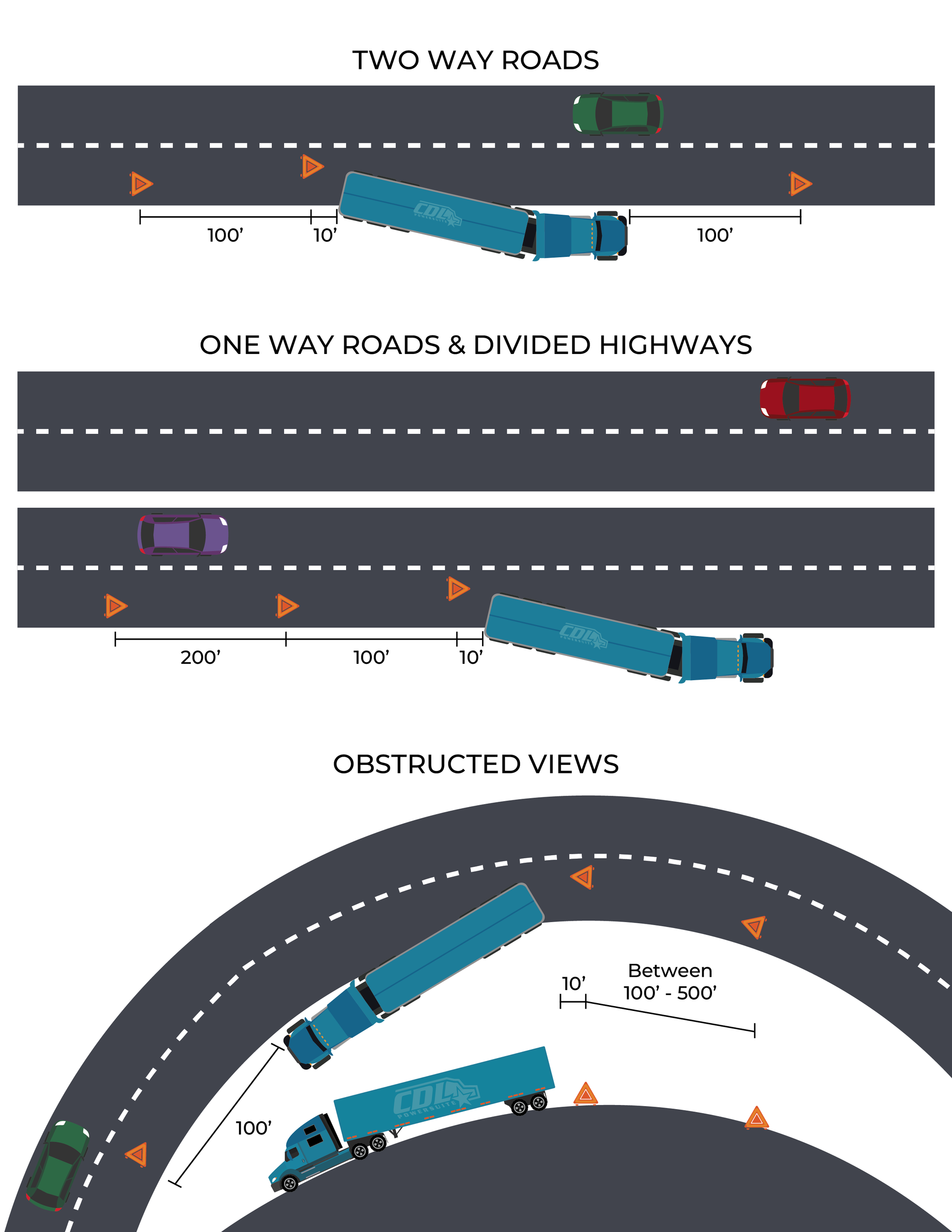
An overview of essential training tips for teaching new CDL drivers how to handle roadside emergencies and correctly place emergency warning triangles. The article breaks down FMCSA-compliant triangle placement procedures for different road types — including two-way roads, divided highways, and obstructed views

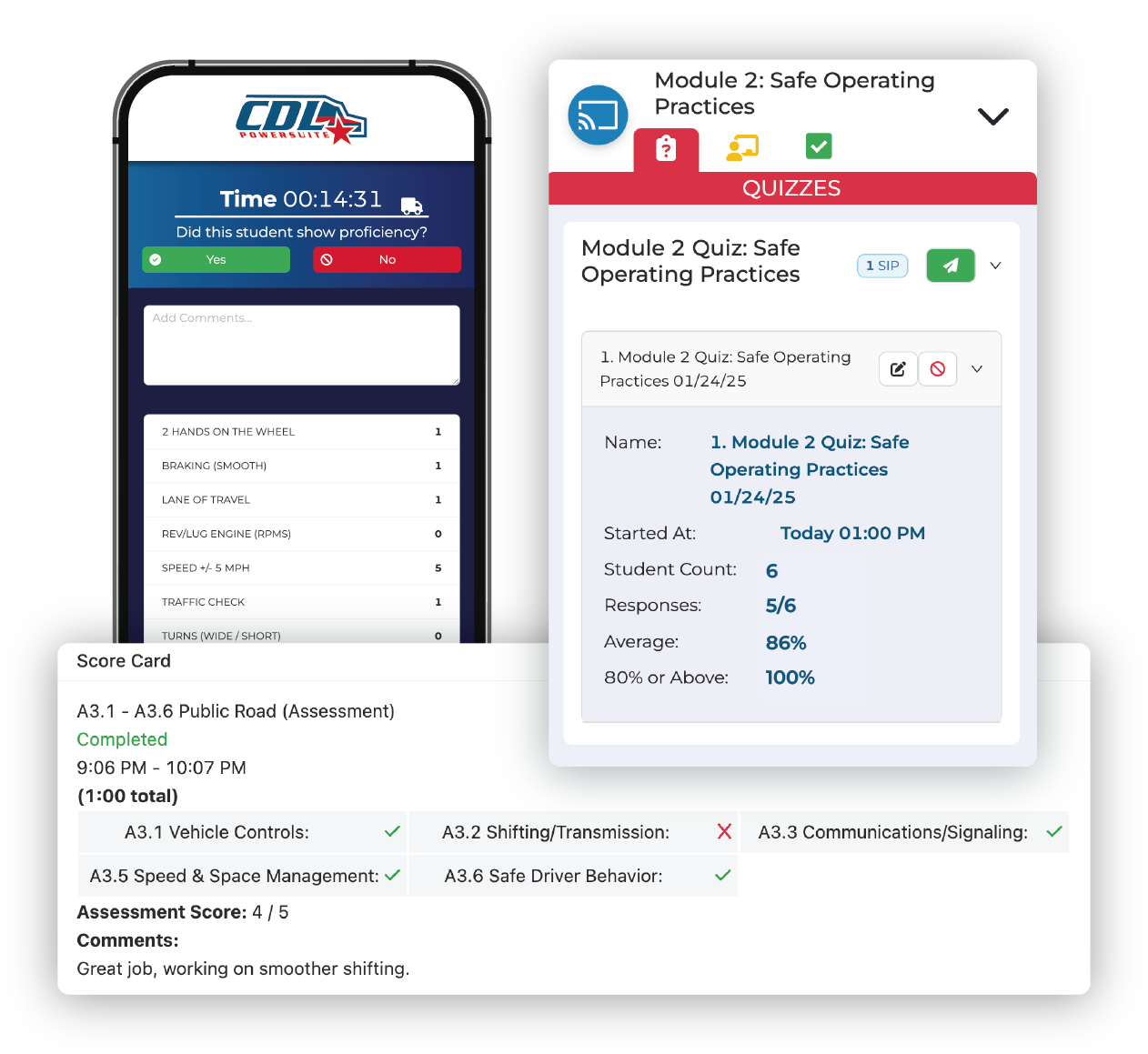
Effective CDL classroom training is essential for preparing future commercial drivers for success. In this article, we explore best practices for CDL schools and in-house trainers, covering how to create engaging presentations, develop effective quizzes, and adjust course material in real time based on student performance.

In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through the registration process, covering eligibility requirements, necessary documentation, and key steps to get your program approved. Whether you’re launching a new training school or developing an internal CDL training initiative, this guide will help you navigate the process with confidence.

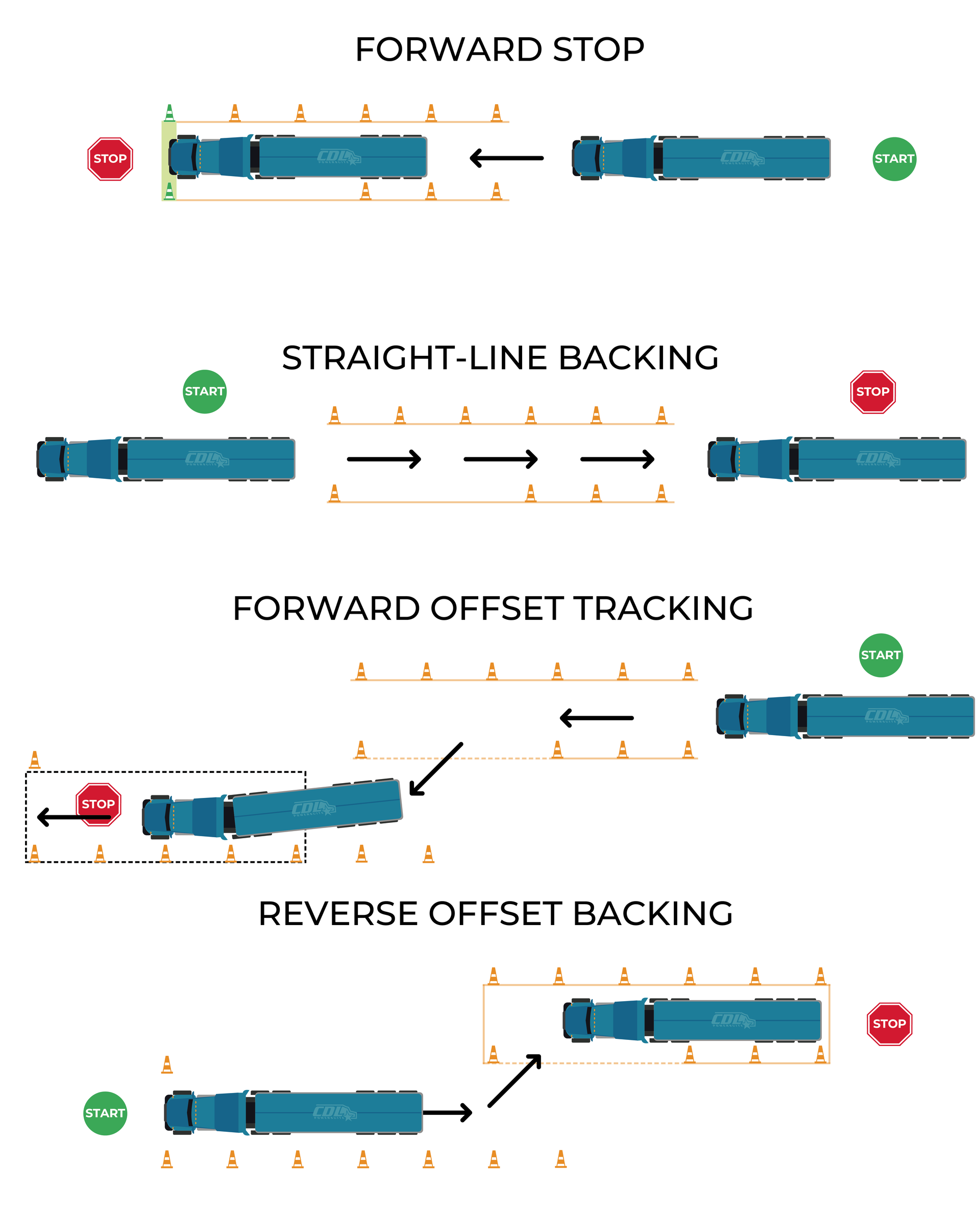
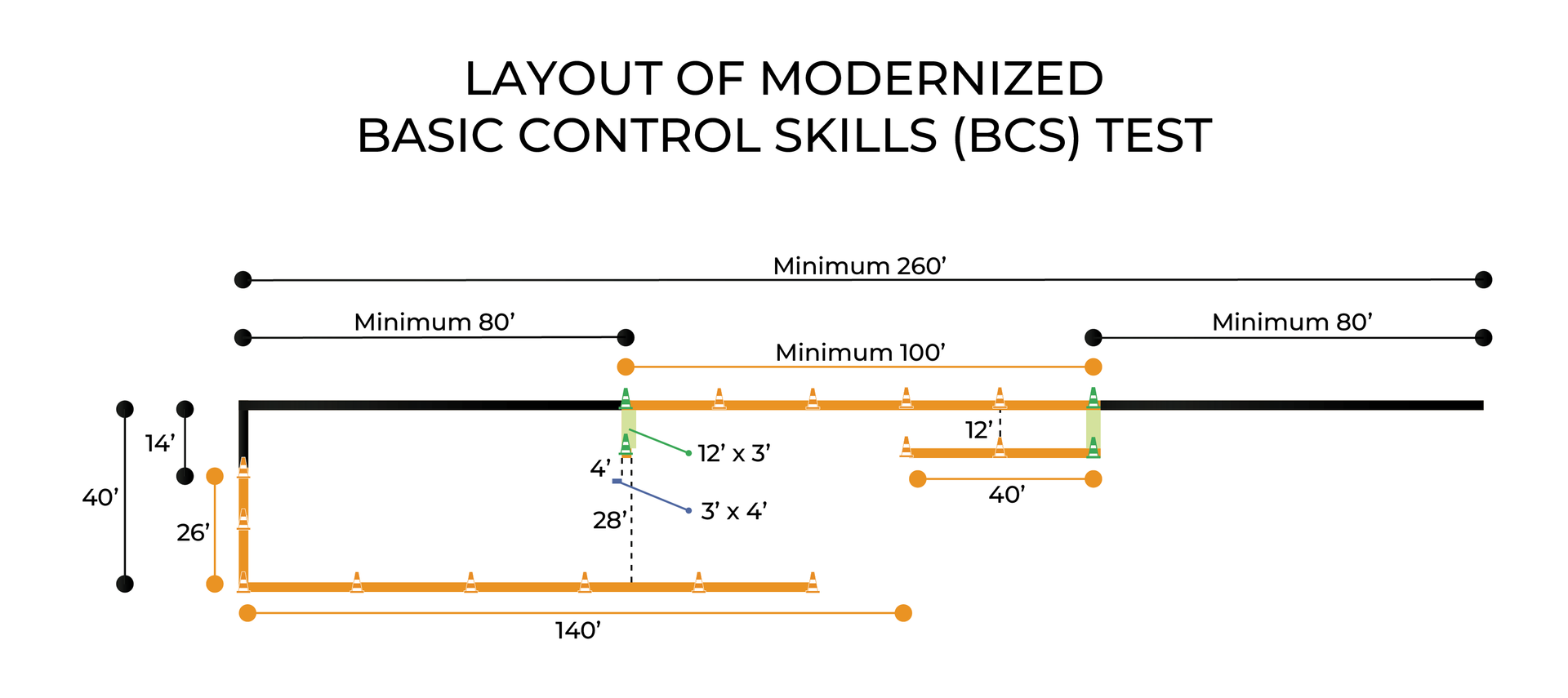
The Modernized Basic Control Skills Test for a CDL evaluates a semi-truck driver's ability to maneuver a commercial vehicle accurately through four exercises: Forward Stop, Straight-Line Backing, Forward Offset Tracking, and Reverse Offset Backing. Success in the test requires precision, adherence to instructions, and effective use of mirrors and pull-ups to avoid penalties for encroachments and improper positioning.

CDL instructors play a critical role in training the next generation of commercial drivers by ensuring students meet FMCSA’s Entry-Level Driver Training (ELDT) requirements. They must hold a valid CDL, complete certification through an FMCSA-registered training provider, and track student progress in both theory and behind-the-wheel (BTW) training. To stay compliant, instructors must maintain proper records, keep their certifications up to date, and adapt to evolving federal regulations to deliver high-quality, standards-compliant training.

The Basic Control Skills (BCS) test is a crucial part of the CDL skills exam, assessing a semi-truck driver's ability to maneuver a commercial vehicle through controlled exercises like backing, turning, and parking. With the FMCSA’s ELDT regulations requiring standardized training, all entry-level drivers must complete a curriculum before testing, ensuring consistent skill levels across states. Proper technique, adherence to test guidelines, and strategic use of pull-ups can help trainees avoid penalties, pass the exam, and develop safe driving habits for real-world trucking.

The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) approved a modernized Commercial Driver's License (CDL) skills test on August 11, 2022, aiming to enhance training efficiency and standardize instruction across programs. This modernized approach consolidates four backing maneuvers into a compact area using the same set of cones, significantly reducing the space required for exercises and allowing training facilities to accommodate more students. While some states have adopted the modernized test, its implementation is at the discretion of individual states, with others planning to integrate it in the coming years.

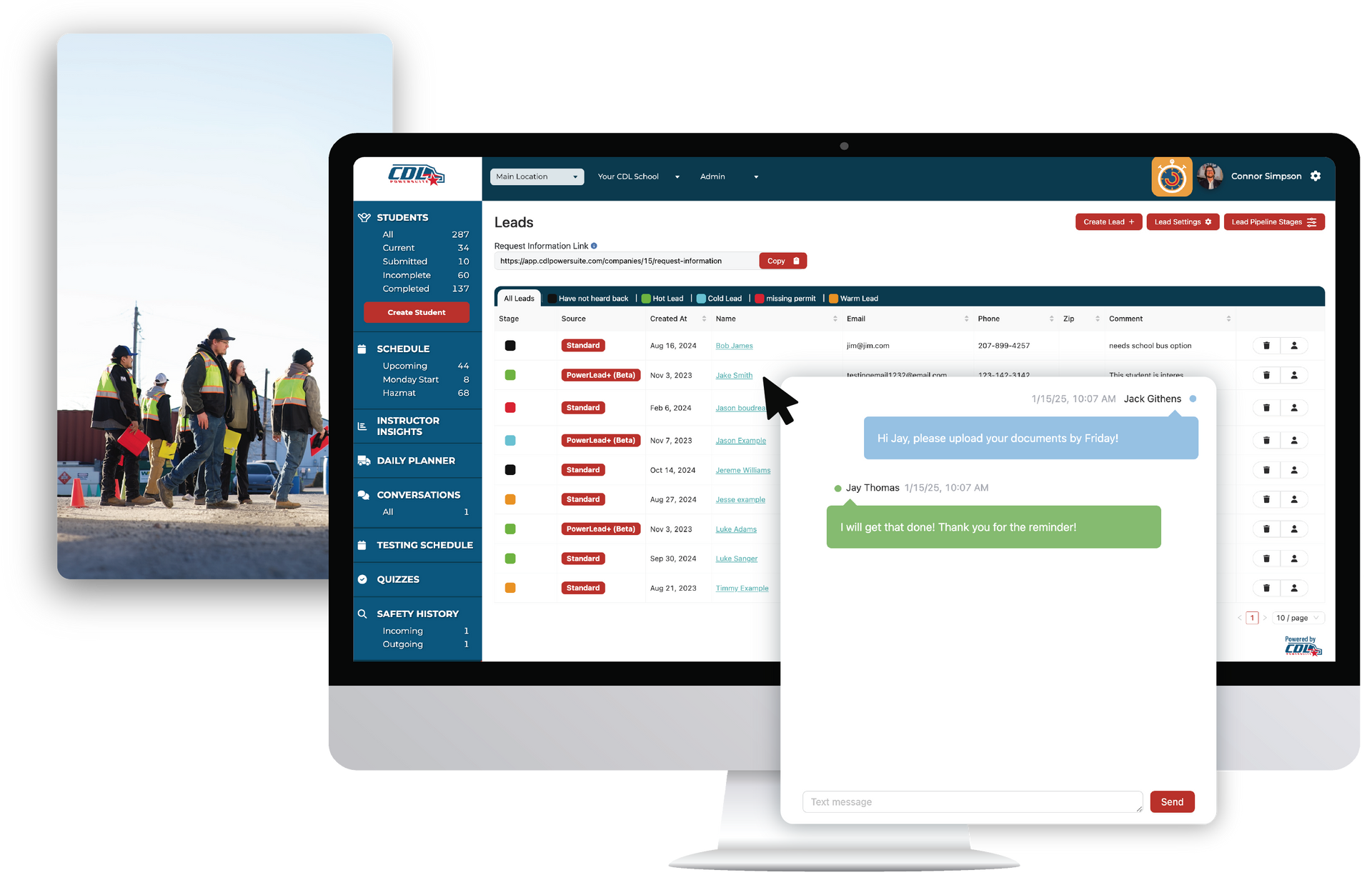
Prompt lead follow-up is crucial for CDL training providers, as studies indicate that contacting leads within 5 minutes makes them 400% more likely to convert. Utilizing multiple communication channels and persistent follow-ups further enhance enrollment rates. Implementing these strategies ensures higher engagement and successful student recruitment.

Tracking student attendance and training hours in CDL schools is essential for compliance, operational success, and FMCSA audit readiness. While the FMCSA does not mandate minimum hours, detailed records help meet state, funding, and employer expectations, often requiring 120 to 160 hours of training. Proper time tracking also supports program evaluation, liability protection, resource allocation, and accreditation efforts, ensuring a well-documented and high-quality training experience.

Effective class scheduling is essential for CDL training programs, ensuring the right balance of students, instructors, and equipment to maximize learning outcomes. Maintaining ideal student-to-instructor ratios—4:1 for road training and 12:1 for range/pre-trip training—enhances personalized instruction, improves pass rates, and prevents instructor burnout. By implementing strategic scheduling practices, monitoring capacity, and optimizing resources, CDL schools can provide high-quality training, strengthen their reputation, and produce skilled, job-ready drivers.

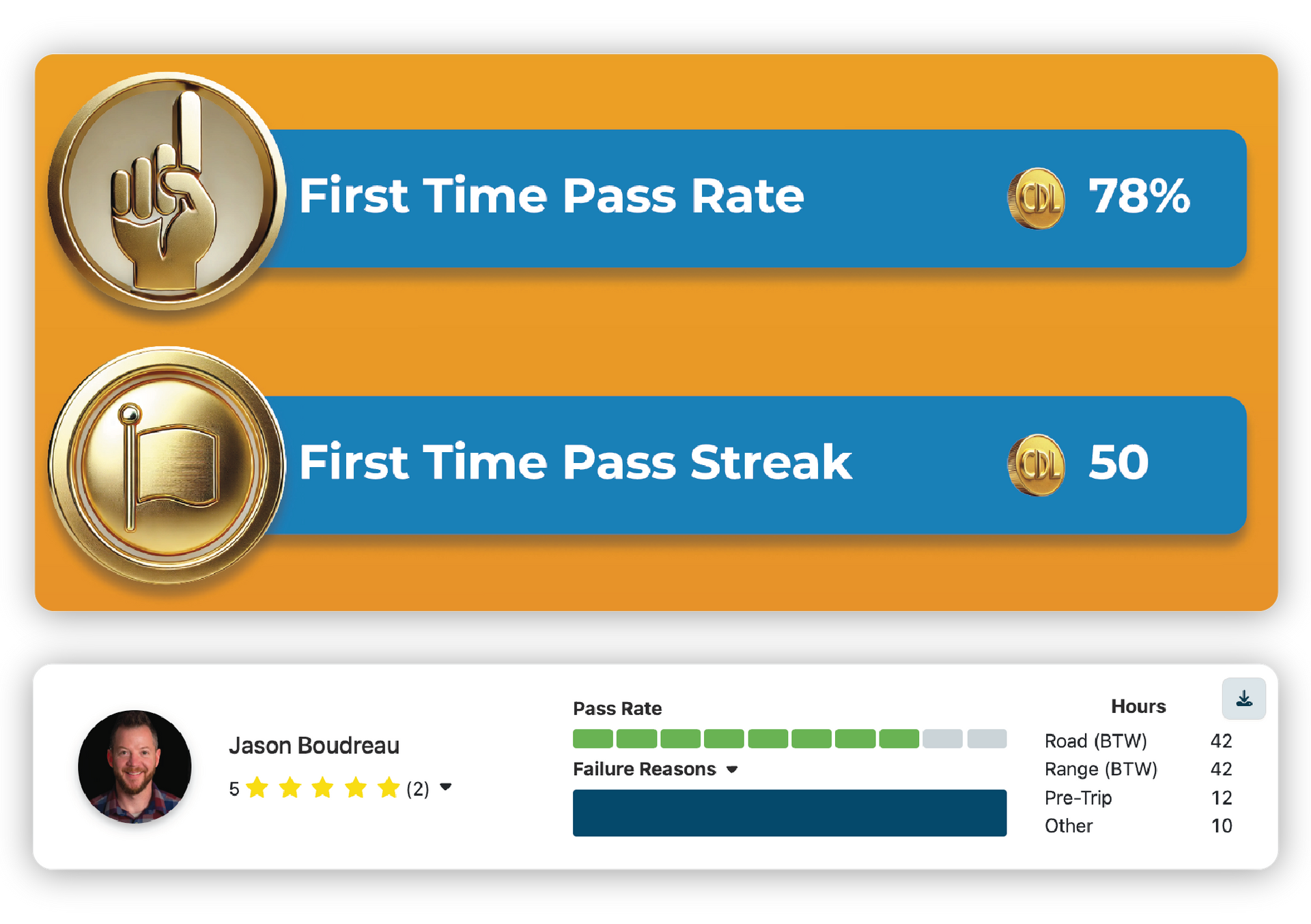
A high first-time pass rate is a critical indicator of a CDL training program's effectiveness, reflecting well-designed curricula and competent instruction. It enables efficient resource allocation by reducing the need for retraining and allows students to transition more quickly into employment, enhancing the school's reputation. To improve this metric, schools should analyze instructor performance, provide targeted support, gather student feedback, and continuously update course materials to align with evolving industry standards.

The FMCSA’s ELDT requirements mandate that CDL training providers cover essential skills like vehicle inspections, basic control skills, safe driving practices, emergency maneuvers, and range exercises. Proper documentation of training completion, student progress, and instructor sign-offs is crucial for compliance and audit preparedness. Maintaining accurate records for at least three years ensures training providers meet FMCSA standards, avoid penalties, and streamline operations with audit-ready documentation.

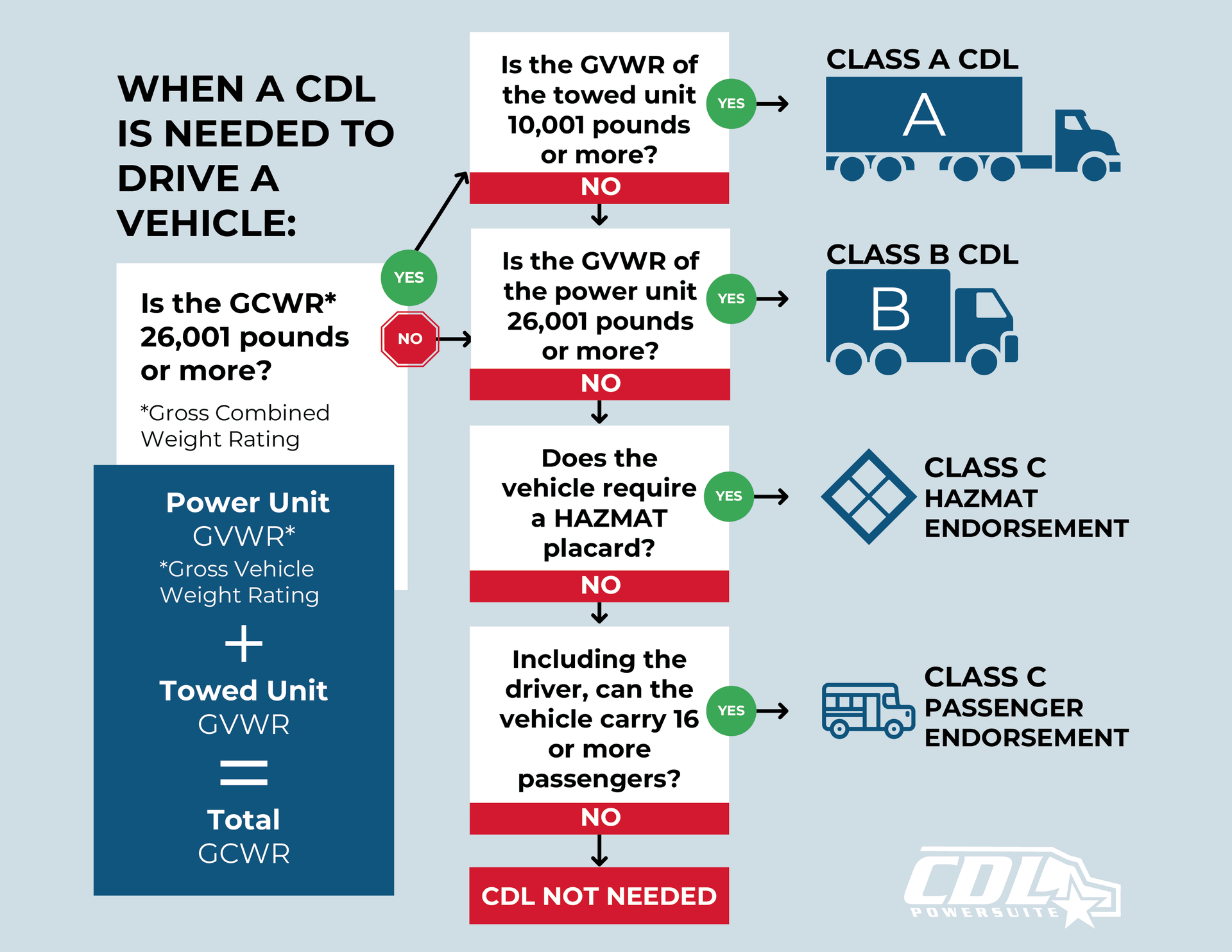
Providing prospective CDL students with a clear understanding of the licensing process and vehicle classifications is essential for informed decision-making and successful training outcomes. Key steps include completing Entry-Level Driver Training (ELDT), passing a Department of Transportation (DOT) physical, obtaining a Commercial Learner’s Permit (CLP), enrolling in behind-the-wheel training, demonstrating proficiency in ELDT units, and passing the state's CDL skills exam. CDLs are categorized into Class A, B, and C, each corresponding to specific vehicle types and requirements.

To comply with FMCSA's Entry-Level Driver Training (ELDT) standards, CDL training providers must collect and maintain specific documents from trainees, including a valid driver's license, Commercial Learner’s Permit (CLP), and Medical Examiner’s Certificate. While not federally mandated, obtaining Motor Vehicle Records (MVRs) and verifying drug screen compliance are considered best practices and may be required by certain states or employers. Training providers are obligated to retain all pertinent records for at least three years post-training to ensure compliance and readiness for potential audits.

Enrollment agreements are essential for CDL training providers, ensuring clarity, accountability, and compliance with FMCSA regulations. These agreements define training terms, attendance expectations, and proficiency requirements, reducing misunderstandings and reinforcing federal compliance standards. Serving as legally binding documents, they protect both providers and trainees while promoting transparency and operational efficiency in CDL training programs.

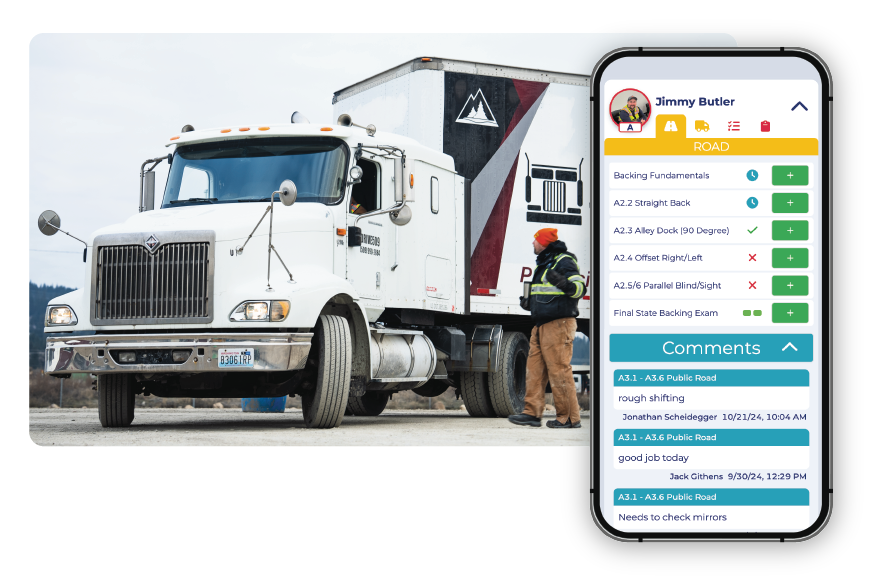
The foundation of any exceptional CDL training program is the instructors. Great educators require the right tools to not only manage the day-to-day, but also to grow as effective, impactful teachers. At CDL PowerSuite, we believe that equipping your instructors with the best resources empowers them to become more efficient, organized, and effective, ultimately leading to better student outcomes. With our newly redesigned Instructor Portal, we’re giving your instructors the tools they need to excel in every aspect of their job

To truly achieve best-in-class CDL training, it’s essential to have the right tools and strategies in place that ensure your instructors can deliver the highest quality instruction while maintaining operational efficiency. As a CDL school owner, lead instructor, or administrator, you know that delivering exceptional training requires more than just an FMCSA ELDT complaint currifulum—it demands a structured, organized approach that allows instructors to focus on teaching while keeping compliance and scheduling seamless.

If you’re a CDL school owner, lead instructor, or administrator, you know that instructors are the lifeline of any successful CDL training program. That’s why it’s crucial to streamline your processes—starting with student registration. With a tailored registration system, you can customize the experience to fit your school’s unique workflow, getting students enrolled faster and more efficiently.

CDL PowerSuite simplifies student enrollment, reduces manual data entry, and ensures compliance. With its centralized daily planner, schools can efficiently manage schedules for instructors, students, and resources, improving organization and cutting costs. Custom branding enhances the school’s professional image, building trust with students and partners. CDL PowerSuite helps create a more efficient and professional CDL training experience.











